-
Review Article
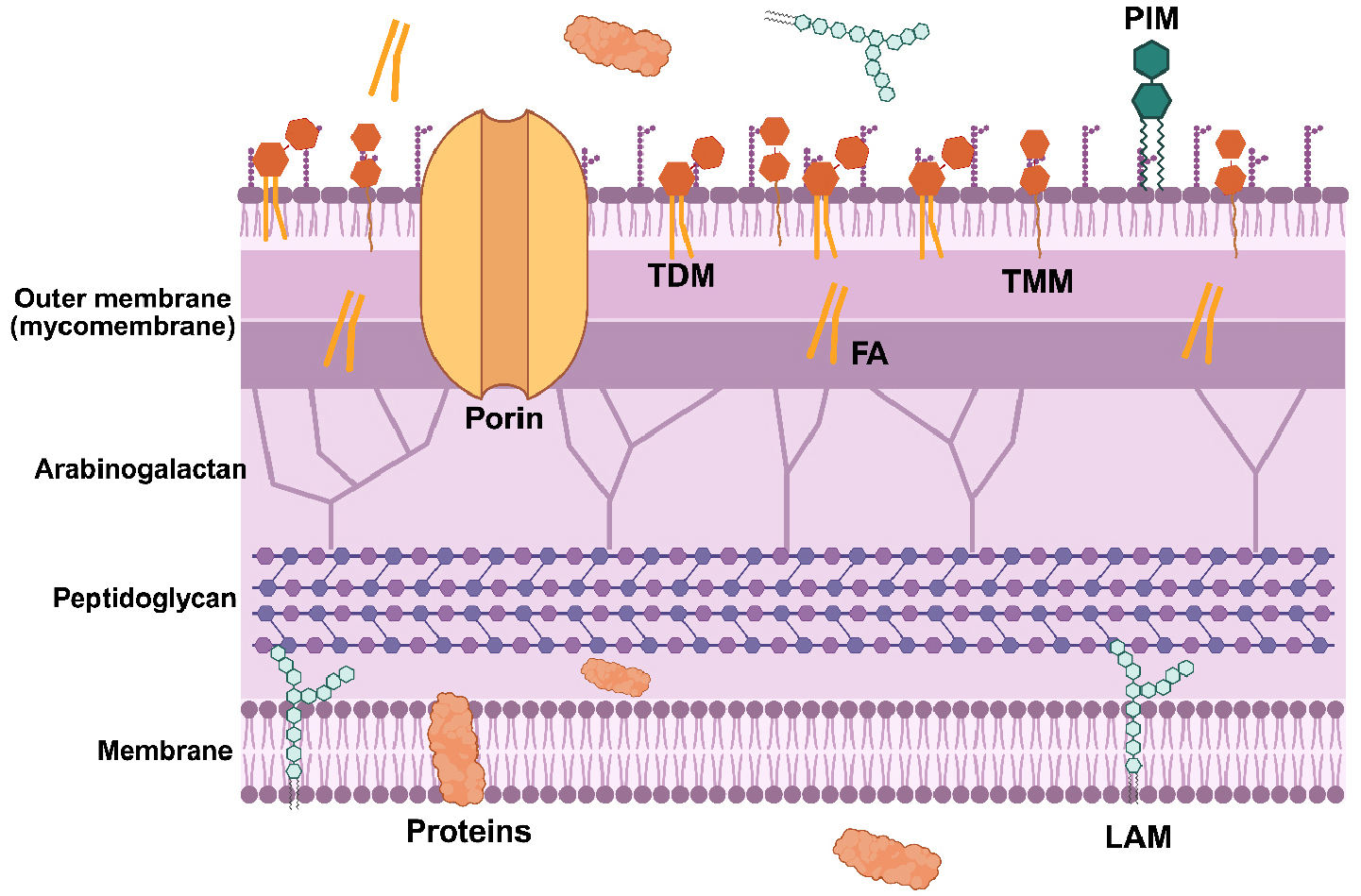
- Diagnostic Biomarker Candidate Discovery using Metabolomics of the Latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Jae Jin Lee, Young Jae Kim, Eun-jin Park, Keun Choi, Hyungjin Eoh
- Tuberculosis (TB) remains a global public health crisis, responsible for approximately 1.3 million deaths annually. The effectiveness of current chemotherapy is limited …
- Tuberculosis (TB) remains a global public health crisis, responsible for approximately 1.3 million deaths annually. The effectiveness of current chemotherapy is limited by its inability to eradicate persister populations of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), a minor fraction of phenotypic variants that exhibit high tolerance to TB antibiotics. Although the mechanisms underlying persister formation are not fully understood, accumulating evidence indicates that intermittent antibiotic exposure and innate immune pressures amplify persister formation, underscoring the importance of persister-specific adaptive metabolism. Mtb persisters arise through remodeling of central carbon and nitrogen metabolism, enabling survival under bactericidal oxidative stresses and facilitating entry into a latent TB infection state. This review summarizes recent advances in understanding the metabolic strategies employed by Mtb persisters to enhance intrinsic antibiotic tolerance and establish latent TB infection. The findings highlight metabolomics as a powerful tool for identifying previously unexplored metabolic signatures of Mtb persisters and for screening potential diagnostic biomarkers of persisters and drug-resistant TB. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article
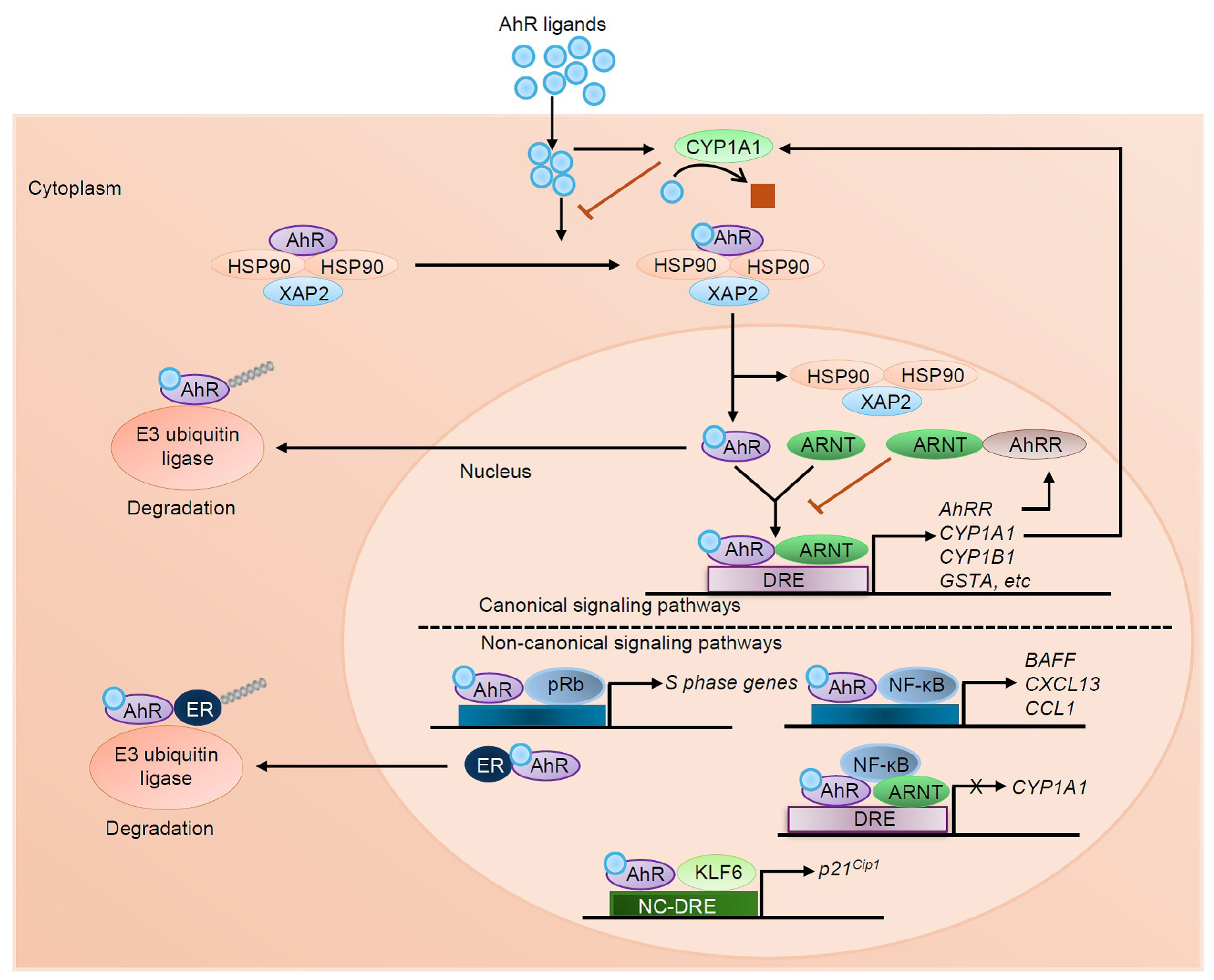
- Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor, a Critical Interface between Host Immunity and Microbiota
- Abdur Rehman, Young-Sang Koh
- The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor first identified for its central role in sensing, mediating responses to environmental …
- The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor first identified for its central role in sensing, mediating responses to environmental pollutants, and xenobiotic detoxification. However, recent studies reclassified AhR as a critical regulator of immune responses, barrier integrity, metabolism, and host-microbiota interactions. The receptor has pleiotropic signaling and is involved in canonical and non-canonical pathways in ligand-, tissue-, and context-specific manners that influence transcriptional programs. AhR is broadly distributed in barrier tissues such as the gut, skin, and lung where it controls both mucosal immunity and tissue homeostasis. It plays important roles in several important physiological processes such as epithelial regeneration, cytokine generation, and T cell differentiation. Additionally, AhR senses microbial tryptophan metabolites, which serves as a critical interface between host immunity and the gut microbiota. Its dualistic role as a mediator of both protective and pathological responses emphasizes its complexity in health and disease. Here, we present an overview of the multiple functions of AhR in regulating immunity and maintaining physiological balance, emphasizing its relevance in both health and disease. We further highlight AhR signaling pathways as therapeutic targets for chronic inflammatory, metabolic, and immune-mediated diseases and provide rationale for developing ligand-specific strategies to achieve optimal efficacy and reduced toxicity in clinical applications. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Article
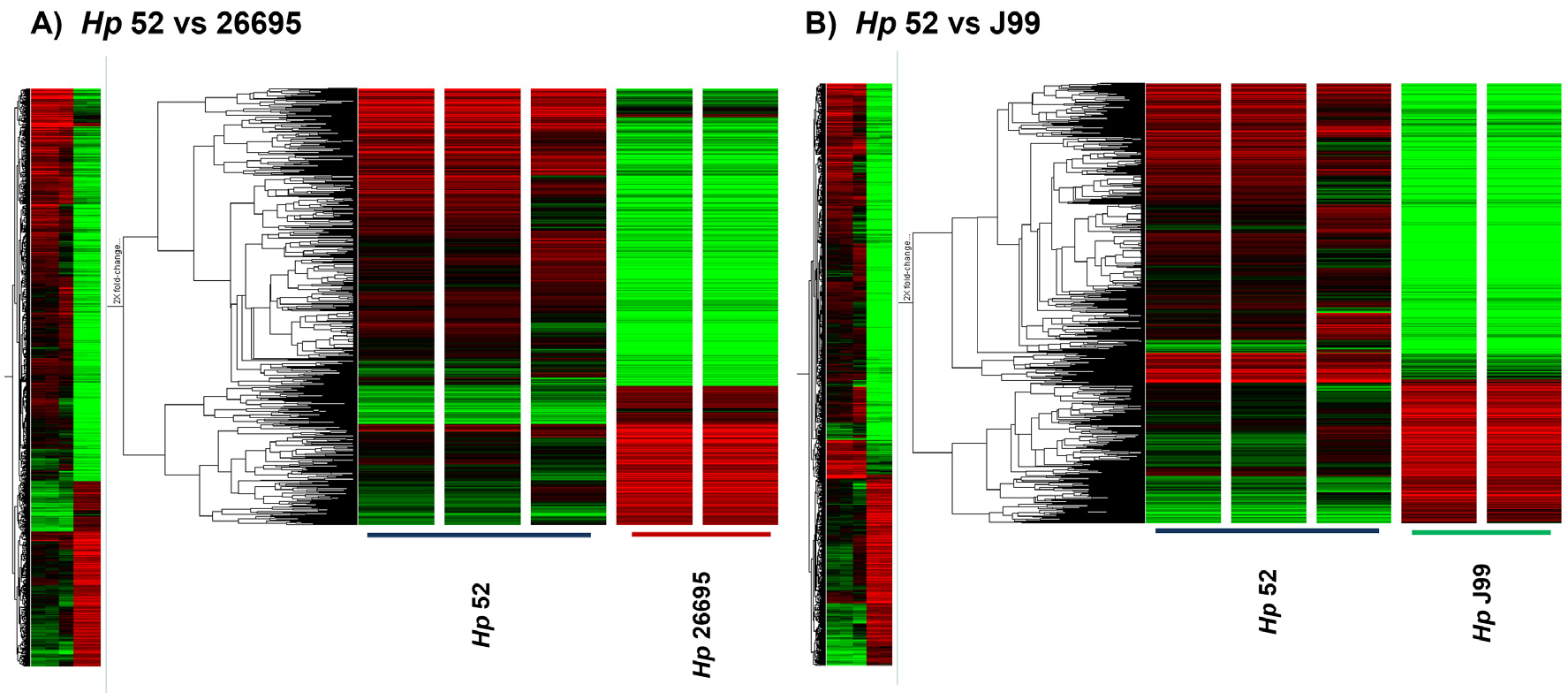
- Identification of Potential Gene Determinants Associated with Mouse Infectivity-Related Immune Modulation in Helicobacter pylori
- Jong-Hun Ha, Jin-Sik Park, Jeong-Gyu Choi, Jeong-Ih Shin, Seorin Park, Dong-Chul Kim, Hyung-Lyun Kang, Kee Woong Kwon, Seung Chul Baik, Min-Kyoung Shin, Myunghwan Jung, Woo-Kon Lee
- Mouse-adapted Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) strains exhibit distinct abilities to colonize the mouse gastric environment, suggesting that strain-specific genetic factors …
- Mouse-adapted Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) strains exhibit distinct abilities to colonize the mouse gastric environment, suggesting that strain-specific genetic factors contribute to host adaptation and immune interaction. This study aimed to find genetic determinants associated with mouse infectivity–based strain differences and to characterize their potential roles in immune modulation using in vitro functional assays. Comparative transcriptomic analyses were performed using microarrays to compare a mouse-infectious H. pylori strain (Hp52) with non- mouse-infectious strains (26695 and J99). Candidate genes were screened based on differential expression patterns associated with mouse infectivity phenotypes. Four genes—HPKB0346, HPKB0407 (acetyl-CoA synthetase), HPKB0424, and HPKB1443 (alanine dehydrogenase, ald)—were selected for further investigation based on their increased expression or strain-specific presence in Hp52. Targeted knockout mutants were generated in the Hp52 using a cross-over PCR and natural transformation. To evaluate immunomodulatory effects in vitro, mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) were stimulated with wild-type or mutant strains, and the expression profiles of cytokines and activation markers were quantified by real-time qRT-PCR. Compared with the wild type, all knockout mutants induced significantly reduced expression of IFN-γ and MHC II in BMDCs. Notably, stimulation with the Δald mutant elicited increases in IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10 expression indicating a distinct immunomodulatory profile. Collectively, these findings suggest that specific genetic factors identified through mouse infectivity–based screening, particularly ald, are associated with the modulation of dendritic cell responses in vitro and may contribute to host adaptation and immune regulation by H. pylori. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Article
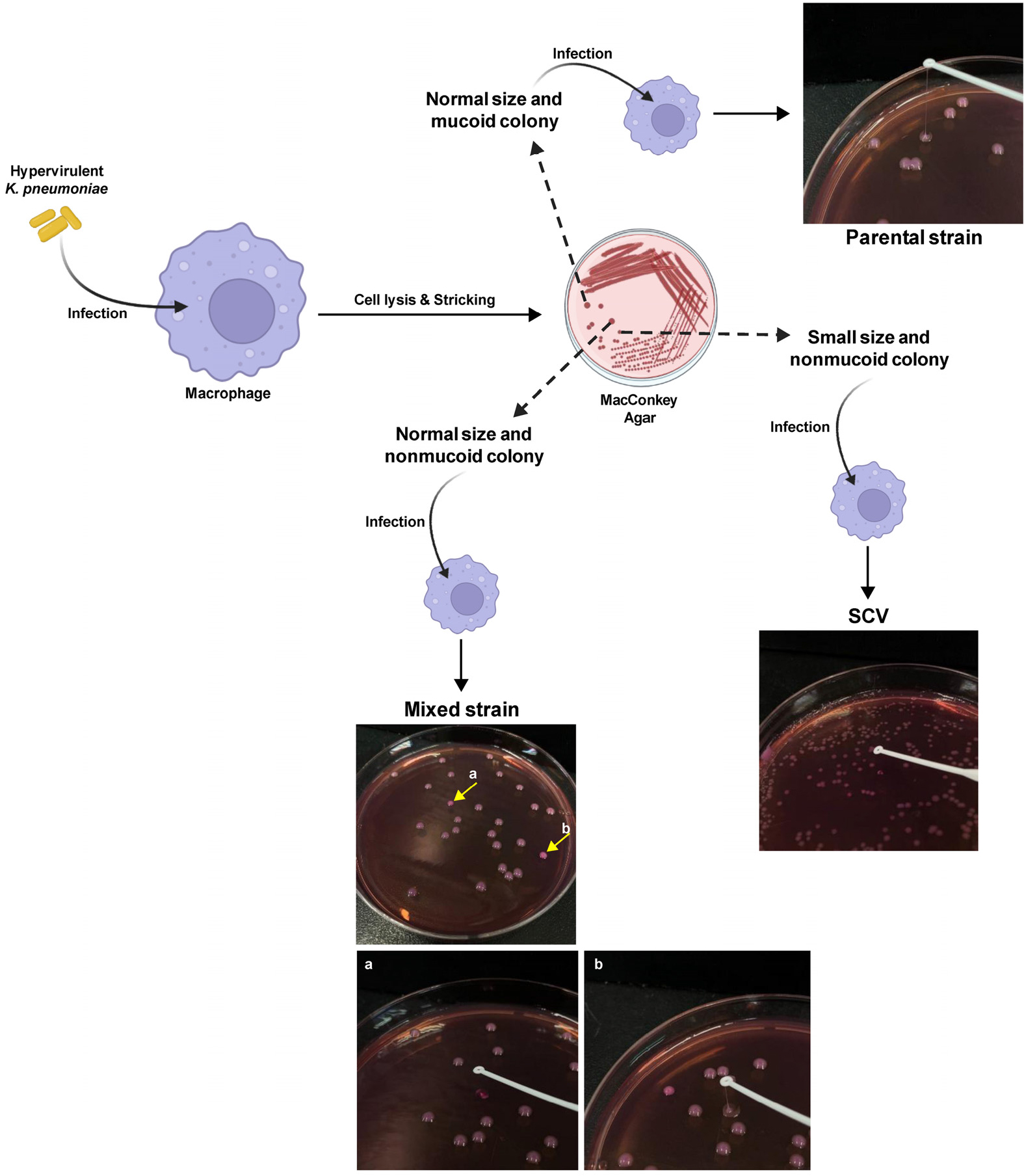
- Phenotype and Antibiotic Resistance Switching in Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Hui-Jung Jung, Ju Yeong Lee, Seulki Kim, Seong Hun Jeong, Miri Hyun, Ji Yeon Lee, Won-Ki Baek, Hyun ah Kim, Jin Kyung Kim
- Phenotypic variation, including reduced capsule production, is common in Enterobacteriaceae. In this study, we investigated phenotypic switching in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae …
- Phenotypic variation, including reduced capsule production, is common in Enterobacteriaceae. In this study, we investigated phenotypic switching in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp). We observed irregular colony morphology, with small colonies displaying reduced mucoviscosity, and identified three variants- parental (mucoid), mixed (nonmucoid, heterogeneous), and a stable small-colony variant (SCV, nonmucoid). Gene expression analysis revealed no significant differences in the expression of capsule and virulence genes between the altered colonies and the parental strain. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) confirmed identical virulence-gene profiles across 11 targets. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing demonstrated a graded increase in polymyxin B resistance in phenotypically altered colonies (parental < mixed < SCV), whereas colistin susceptibility differed among variants, with the mixed population exhibiting increased susceptibility. All variants were susceptible to gentamicin and meropenem. Furthermore, functional assays using murine macrophages showed that nonmucoid variants exhibited significantly enhanced phagocytosis and intracellular survival compared with the mucoid parental strain. These findings highlight the dynamic phenotypic plasticity of hvKp and suggest that capsule-deficient variants acquire distinct survival advantages within host cells, accompanied by altered antimicrobial resistance profiles and trade-offs between extracellular immune evasion and intracellular persistence. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Article
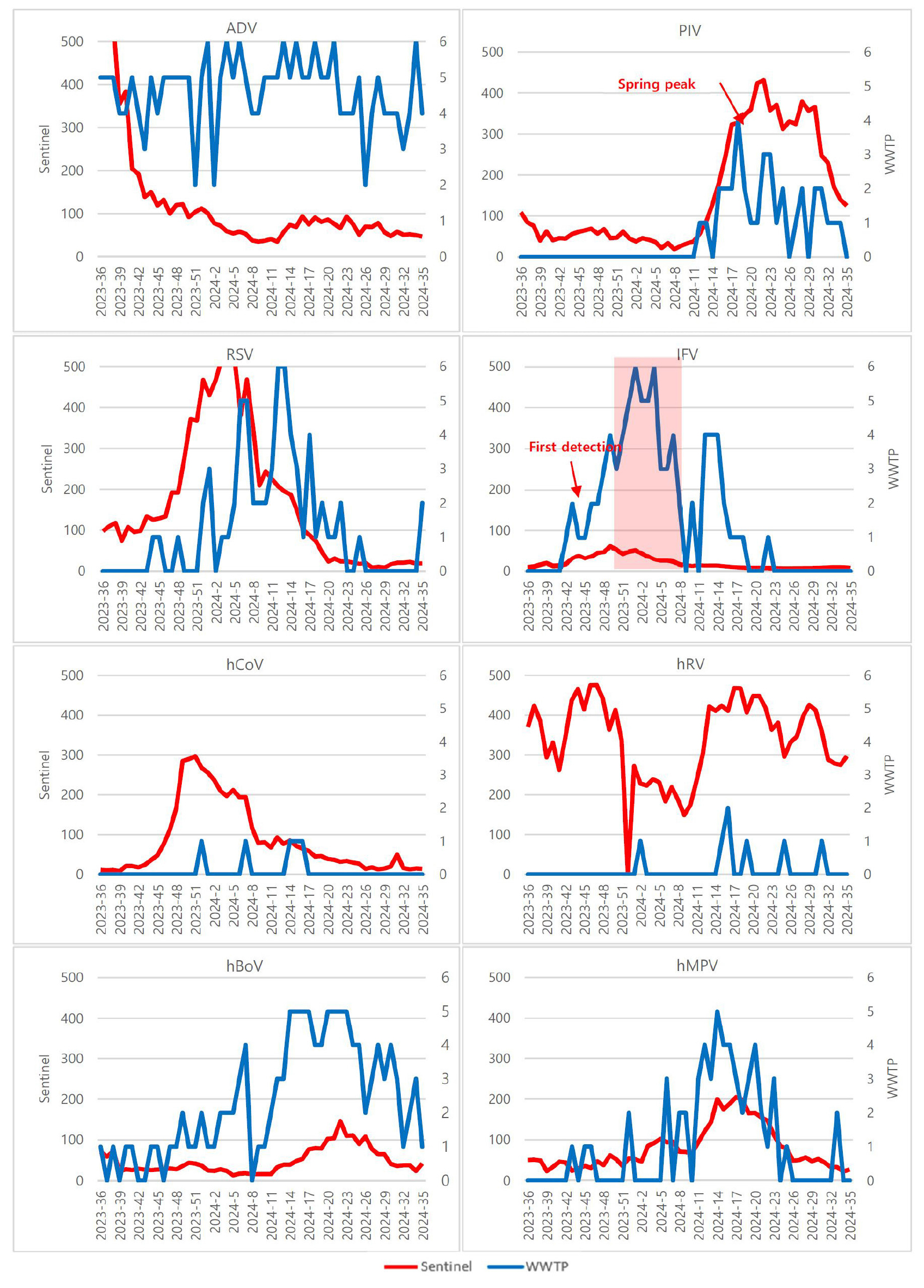
- A Correlation Study of Acute Respiratory Virus Detection in Wastewater and National Sentinel Surveillance
- Hyeon-Jin Kim, Yeong-A Jeong, Hee-Soo Koo, Byung-Jun Kim
- Effective surveillance of acute respiratory viruses (ARVs) is crucial for timely public health action, yet sentinel systems have intrinsic gaps in coverage …
- Effective surveillance of acute respiratory viruses (ARVs) is crucial for timely public health action, yet sentinel systems have intrinsic gaps in coverage and reporting timeliness. Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) can complement sentinel networks by capturing population-level viral circulation regardless of healthcare- seeking behavior. We conducted a correlation study between ARV detections in influent wastewater and national sentinel surveillance in Korea. From September 2023 to August 2024, 295 influent samples collected weekly from six wastewater treatment plants in Busan were tested for eight ARVs by multiplex real-time RT- PCR, while nationwide sentinel case counts were analyzed in parallel. Adenovirus (81.4%) and human bocavirus (41.0%) were persistently detected, whereas influenza virus (27.8%) and human metapneumovirus (19.0%) showed clear seasonal peaks. Pearson correlation demonstrated strong agreement for human metapneumovirus(hMPV)(weekly r = 0.770; monthly r = 0.955; |r| ≥ 0.7), parainfluenza virus (PIV) (weekly r = 0.749;monthly r = 0.661), and influenza virus (IFV)(weekly r = 0.710; monthly r = 0.612), with moderate associations for huma bocavirus(hBoV). These results indicate that WBE reliably reflects temporal trends for clinically important ARVs and can augment sentinel surveillance. Correlation patterns also help identify ARVs most suitable for wastewater monitoring, informing prioritization in public health applications. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Article
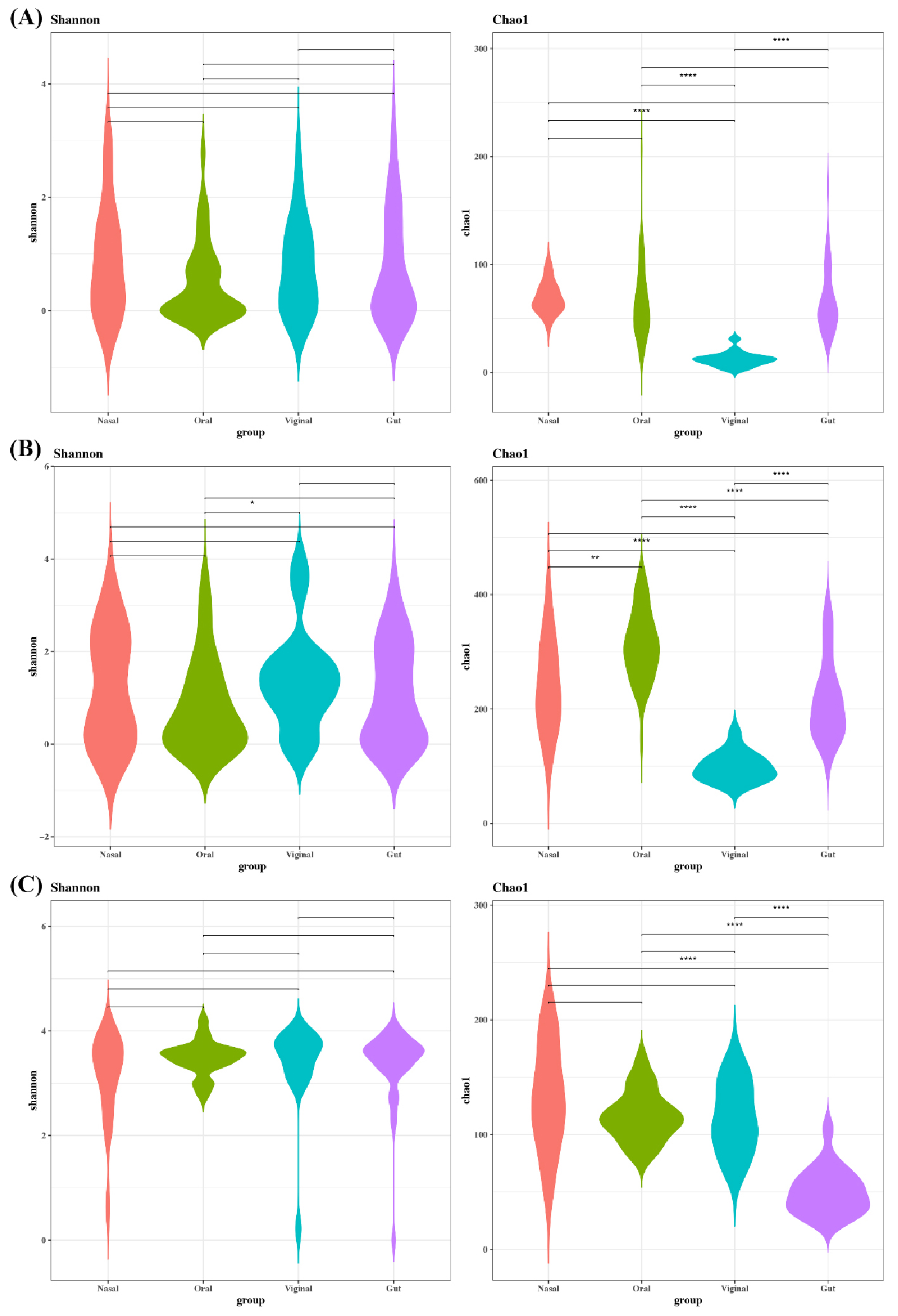
- Benchmarking Read-Based Virome Profilers for Human Virus Detection and Community Discovery
- Na Rae Choi, Jung Hwa Park, Tae Sung Kim, Hee Sam Na
- Background: Shotgun metagenomics enables human virome profiling, yet read- based platforms differ in databases and mapping strategies, potentially altering biological conclusions, …
- Background: Shotgun metagenomics enables human virome profiling, yet read- based platforms differ in databases and mapping strategies, potentially altering biological conclusions, especially when goals diverge between human virus detection and broader virome discovery. Methods: We benchmarked Kraken2, FastViromeExplorer, and ViromeScan on whole-genome shotgun datasets from gut, nasal, oral, and vaginal sites. Reads were trimmed, human-depleted, and profiled; counts were normalized to CPM. We compared alpha diversity, beta diversity, and taxonomic composition. Results: Platform choice strongly affected viral composition. FastViromeExplorer produced the highest CPM and alpha diversity. Kraken2 was intermediate, and ViromeScan was lowest. Beta-diversity showed clear site clustering for all platforms, strongest with FastViromeExplorer, moderate with Kraken2, and weakest with ViromeScan. At the phylum level, Uroviricota dominated Kraken2 and FastViromeExplorer, whereas ViromeScan emphasized Nucleocytoviricota and Peploviricota. Genus and species calls were highly platform-dependent. FastViromeExplorer detected the most taxa overall, while ViromeScan preferentially reported eukaryotic and human viruses. Conclusions: Read-based profilers yield divergent virome portraits driven by database scope and mapping stringency. For clinical human-virus detection, curated human and eukaryotic references with coverage-based confirmation are essential. Our results provide practical guidance for aligning pipelines to study goals and underscore the need to report parameters, database versions, and cross-platform validations when interpreting the human virome. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Article
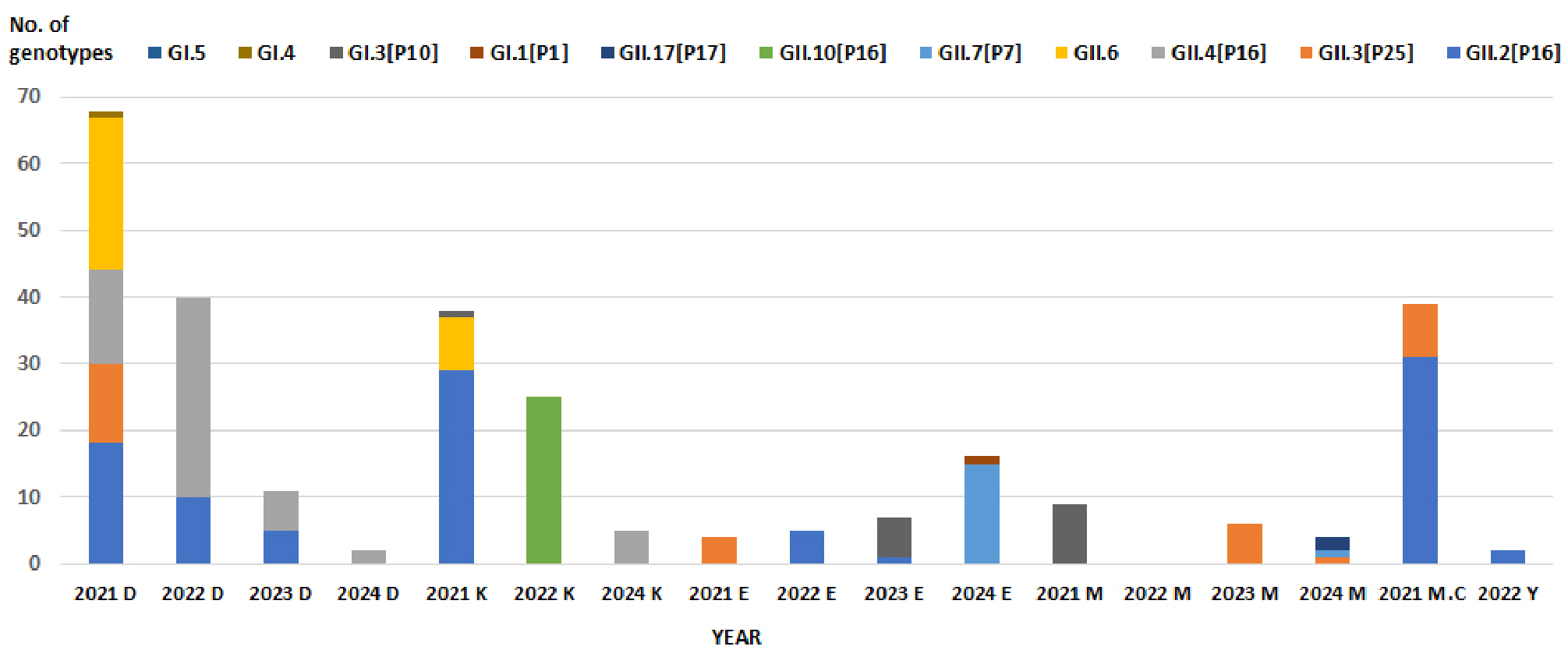
- Molecular Epidemiology of Norovirus Outbreaks in Food-Catering Facilities in Busan, 2021–2024
- Hee-Soo Koo, Hyeon-Jin Kim, Seon-Young Kim, Jung-Hye Choi, Byung-Jun Kim
- Norovirus is the leading cause of foodborne illness outbreaks worldwide and represents a significant public health concern. Highly contagious and responsible for …
- Norovirus is the leading cause of foodborne illness outbreaks worldwide and represents a significant public health concern. Highly contagious and responsible for acute gastroenteritis, norovirus spreads rapidly through contaminated food, water, and direct person-to-person contact. Owing to extensive genetic diversity, individuals may experience repeated infections, with limited cross-protection across genotypes. This study investigated the molecular epidemiology of norovirus outbreaks in food-catering facilities in Busan, Korea, from 2021 to 2024. Among 1,546 stool specimens analyzed, 394 (25.5%) tested positive, comprising 19 genogroup I (4.8%) and 375 genogroup II (95.2%) strains, which represented 12 genotypes (5 GI and 7 GII). Outbreaks occurred most frequently in childcare centers, elementary schools, and kindergartens. Although annual variation in genotype prevalence was observed, GII.4 remained the predominant strain throughout the study period. In 2024, GII.7 was identified for the first time, consistent with strains detected in patients with acute diarrhea in Busan, and GII.17—previously responsible for large outbreaks more than a decade earlier—also re-emerged. These findings underscore the dynamic circulation of norovirus genotypes in community settings and highlight the importance of continuous molecular surveillance. Such efforts are essential for the early detection of emerging variants, improved outbreak prevention, and the development of effective vaccines targeting persistent and high-burden genotypes such as GII.4. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Article
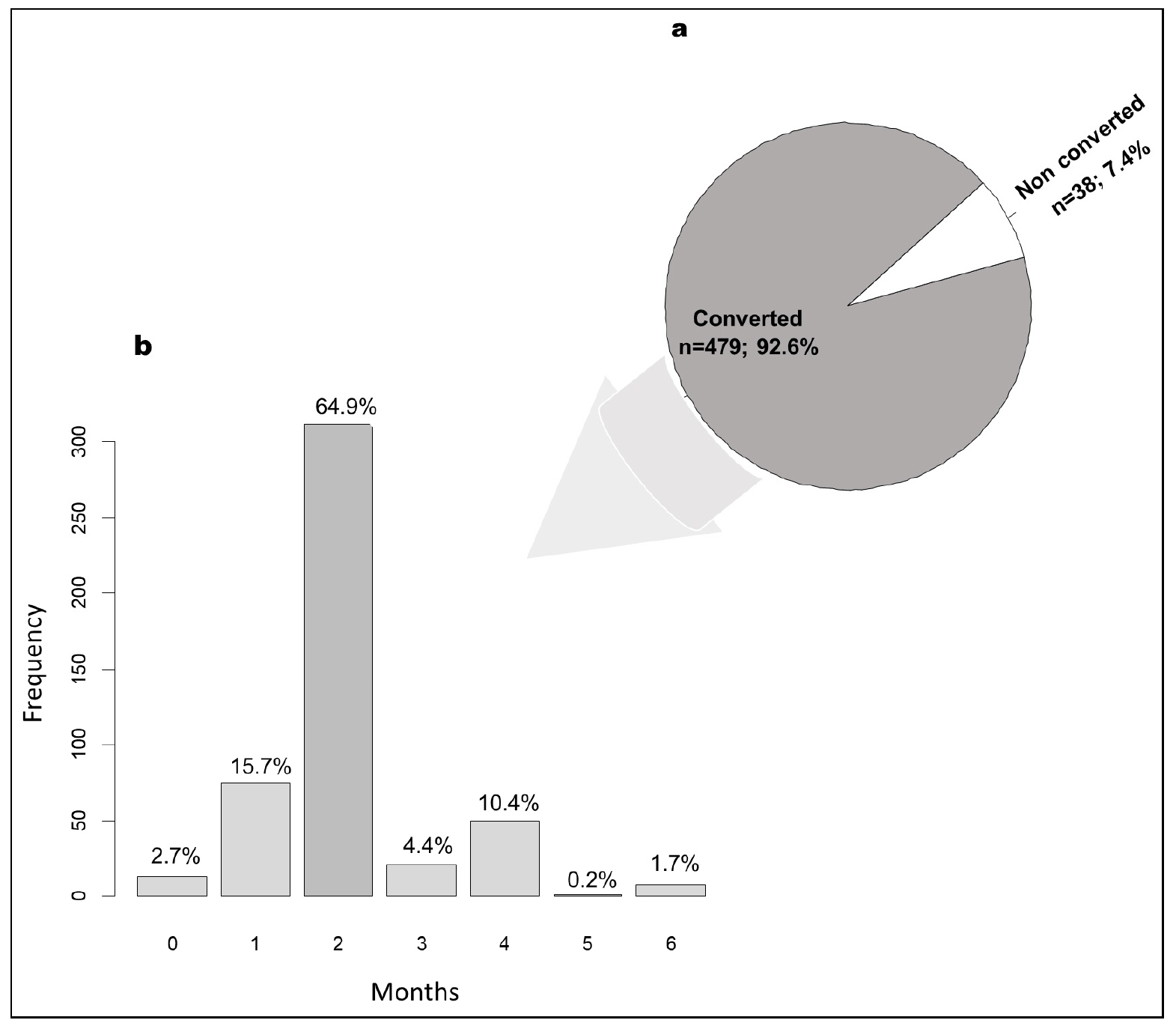
- Time to Sputum Culture Conversion and Associated Factors in Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients in Niger
- Yacouba Abdourahamane, Abdou Natali Bassirou, Ounoussa Tapha, Moussa Abdoul-Nasser, Souleymane Bassirou, Moussa Saley Sahada, Soumana Alphazazi, Adam Mamoudou, Saidou Mamadou
- Background: Culture conversion is a key indicator for monitoring the success of treatment in patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), and enables …
- Background: Culture conversion is a key indicator for monitoring the success of treatment in patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), and enables the daily dose of drugs to be adjusted. This study aimed to determine the sputum culture conversion time of MDR-TB patients and their related factors in Niger. Methodology: A retrospective study was conducted among MDR-TB patients from 2008 to 2020. GeneXpert, culture, and drug susceptibility tests were performed for each patient. A multivariate logistic analysis was performed to determine factors associated with sputum culture conversion. A p-value < 0.05 was considered significant. Results: A total of 517 patients with MDR-TB followed up in various MDR-TB units in Niger were included. These patients consisted of 83.2% males with a mean age of 34±11.8 years. The frequency of culture conversion after initiation of treatment was 92.8%, with 15.7% in the 1st month and 64.9% in the 2nd month. In multivariate logistic analysis, the predictive factors positively associated with delayed culture conversion were age over 40 years (odds ratio = 3.70; 95% CI: 1.47 - 9.60; p=0.006), death (odds ratio =30.13; 95% CI: 10.61 - 96.72; p<0.001), and resistance to ofloxacin 800 mg (odds ratio =26.37; 95% CI: 6.72 – 108.00; p<0.001). Conclusion: This study underscored a relatively high rate of culture conversion during the intensive phase of treatment among patients with MDR-TB in Niger. High age, death, and ofloxacin resistance were identified as risk factors for delayed culture conversion. These results suggest that early intervention in MDR-TB patients can lead to sputum culture conversion and treatment success. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY













